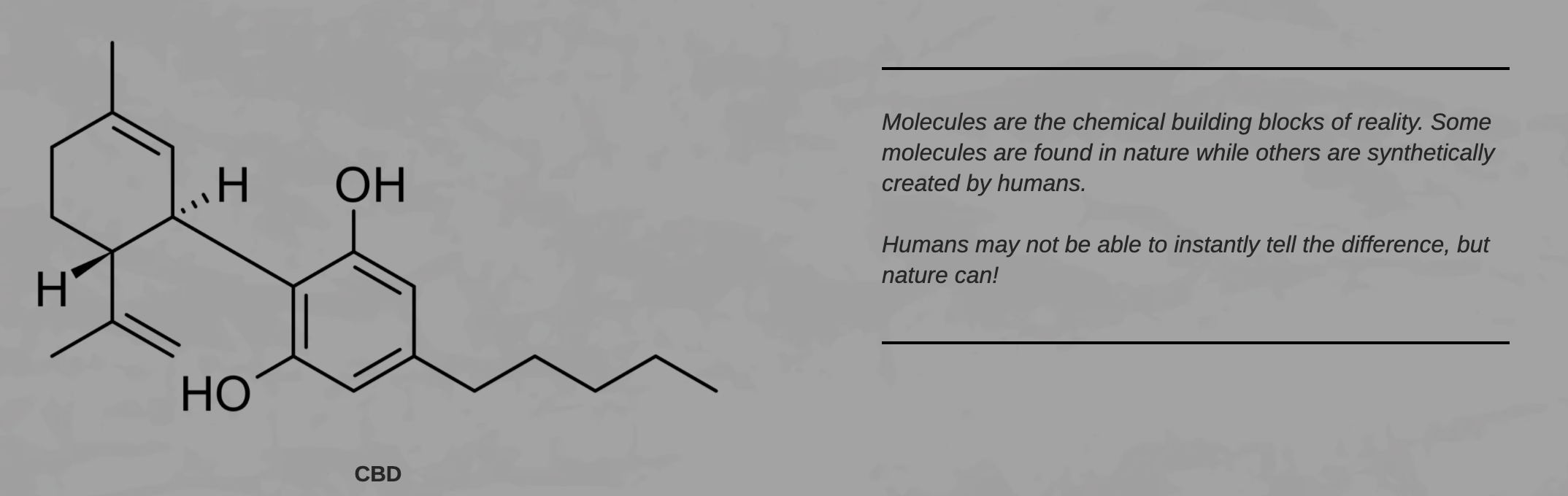
Synthetic CBD vs. Natural CBD: What's
the Difference?
by Dr. Bomi Joseph, Ph.D.
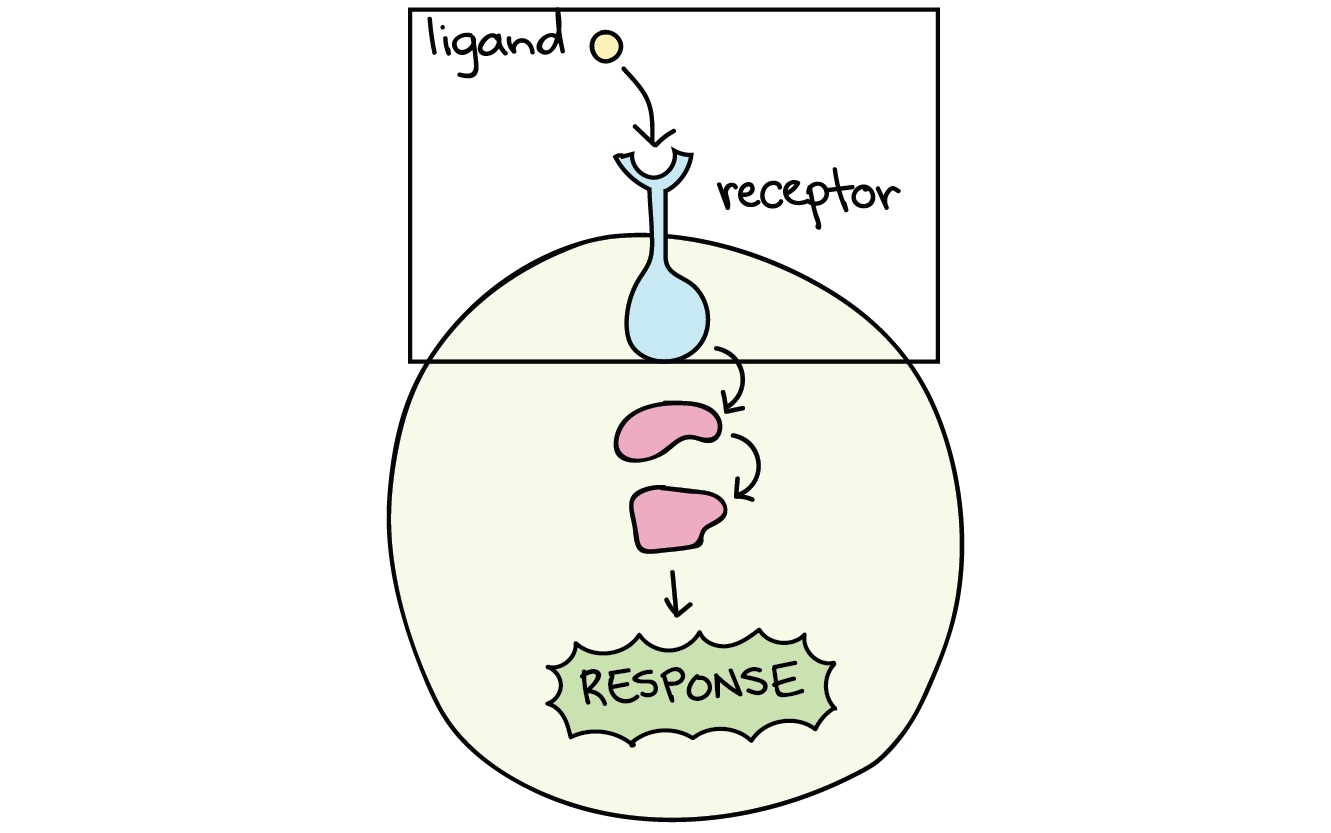
Ligands vs. Receptors
Inorganic molecules such a water and alcohol behave simply, like magnets. Different positively charged ions will stick to negatively changed ions. Complex organic molecules have much more complicated interactions. Inside the body, a molecule that causes an effect or a brings about a reaction called is a “ligand.”
Different compounds in nature like odors, pheromones, plant compounds, hormones or neurotransmitters act as ligands and they send very specific signals that are interpreted by our body. The signal strength is known as “bioactivity.” The compounds in the stalks of a wild hemp plant have very low bioactivity but hybrid cannabis flowers have very high bioactivity.
Cannabinoids Affect Multiple Organs & Receptors
A cayenne pepper contains capsaicin molecules that activate the TRPV1 receptor in our mouth. When cayenne touches our tongue, it sends sensations of “heat” to the brain and it triggers a chain reaction that causes sweating in order to cool ourselves.
The pharmaceutical industry understands the effects of the main “conventional” neurotransmitters (such as serotonin, dopamine and GABA) very well and they have developed thousands of drugs that mimic their activity. But cannabinoids, which are not nearly as well researched due to past prohibition laws and social taboos, can act as both a neurotransmitter and a hormone.
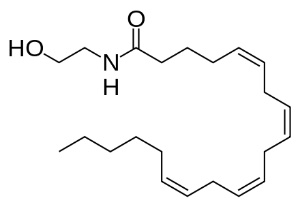
Anandamide, one of our body’s internal cannabinoids, specifically stimulates our CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors.
There are more than 80 cannabinoids in the hemp plant and only two of them, THC and CBD, have been even partially studied in any depth.

There are more than 80 cannabinoids in the hemp plant and only 2 of them, THC and CBD, have been even partially studied in any depth. There are more than 1000 receptor sites – both known and unknown – that these cannabinoids act on. All the permutations and combinations (80+ cannabinoids x 1000+ receptors) make for literally millions of possible signals than can be sent out from a single herb.
The receptors are in all different organs, ranging from the bones to the brain, and the same ligand can have a different effect on different organs.
Why is CBD So Important?
CBD is a ligand that affects the CB2 cannabinoid receptor. Crucial organs like our digestive system, heart and blood have a dense collection of CB2 receptors. The CB2 receptor is also very prevalent in the parasympathetic nervous system which affects many things we can’t consciously control such as:
Visual sense
Taste (gustatory) sense
Smell sense
Behavior & mood regulation
Immune system
Inflammatory system
Autonomous nervous system
Cell density sensing
Homeostasis modulation
Growth & metastasis of some tumors
Endocrine system
A liver cell has CB2 receptors on it, but when it goes rogue and becomes a cancer cell, the number of CB2 receptors tends to increase exponentially. This increase in CB2 receptors tells me that the cancer cell “knows” it is in a very hostile environment an it is under fire from the immune system. The CB2 receptor is critical for its survival of all cells, both normal and malignant.

The Human Inclination to Mess with Nature
Humans and nature are very complementary. But we humans have a crazy inclination to mess with nature such as when we make margarine – taking cheap natural vegetable oils (double “cis” bonds with less hydrogen ions) and trying to simulate more expensive animal fats like butter (single bonded with more hydrogen ions). So food chemists artificially add hydrogen to vegetable oils but this doesn’t really approximate nature – the bond is twisted into a “trans” bond. This twisted bond is foreign to the human enzyme system which only recognizes “cis” bonds found in natural fats. So you get this large, unwieldly fat molecule in the bloodstream that the body doesn’t know how to work with as well. The trans fat unit has a greater tendency to latch on to the cell wall if there is inflammation present, and it can greatly contribute to arteriosclerosis. By tinkering with the chemistry of nature’s fats, humans created a serious public health issue and it took the FDA more than 40 years to restrict the use of trans fats.
Many processed foods contained trans fats until they were banned by the FDA in 2018.
Humans chemists have never been able to perfectly replicate a natural molecule.
A close simulation is a “synthetic” molecule.
Our DNA Recognizes Naturals & Distrusts Synthetics
Humans evolved from plants and we share much of the same DNA. A human being and banana share 60% of the exact same genes and our body intrinsically recognizes the molecular geometry of the sugars and vitamins in a banana as naturally and friendly.
Our DNA and our body innately recognize slight imperfections in patterns and this is helpful for our survival. Our immune system is perceptive enough to pick up on a very slight mutations that a virus has undergone and recognize it as the same threat it encountered once before. When the body encounters an unnaturally “distorted” molecule it doesn’t quite know what to do with it. In a best case scenario, you can get a muted response where there is a very slight positive response. In other cases, your body can have a negative reaction or ignore the molecule completely – causing side effects or wasting your money.
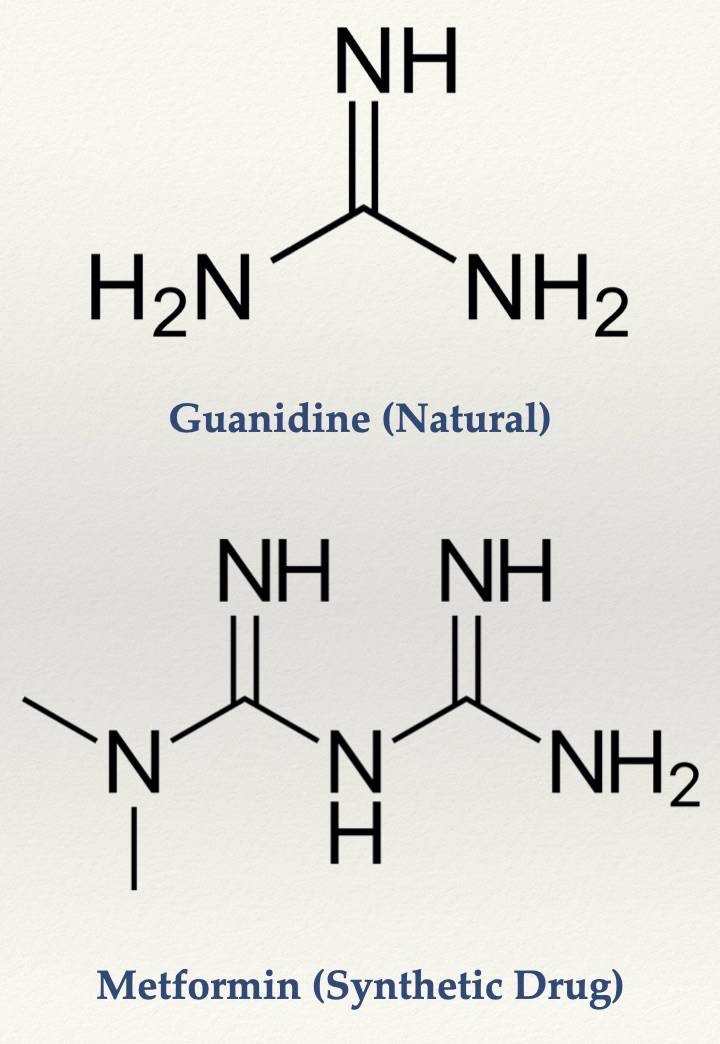
Nature-made Phytoceuticals vs. Synthetic Drugs
Most natural active plant compounds (phytoceuticals) have a long history of human use, they are safer and less toxic, and the body doesn’t reject or react as strongly to them.
Natural compounds are made by nature and they can’t be patented. The pharmaceutical industry uses plant molecules for inspiration and they often develop synthetic drugs “inspired” by nature which can patented and profited from. These drugs almost always have more side effects than their natural siblings, because the body recognizes them as ‘distorted’ and not-quite-legitimate molecules. They’re more toxic and you are much more likely to develop a tolerance to synthetic drugs, which have a very short history of human use, and you can easily develop cravings or addiction. There can also be very severe negative reactions, such as birth defects or death, so all new synthetic drugs are required to pass extensive trials and testing.
It’s not really a good idea to take a pharmaceutical drug for more than 3 weeks and 3 months is an absolute maximum recommended duration. I don’t agree with the way that drugs are recklessly overprescribed in the United States and I don’t think our bodies like it much, either.
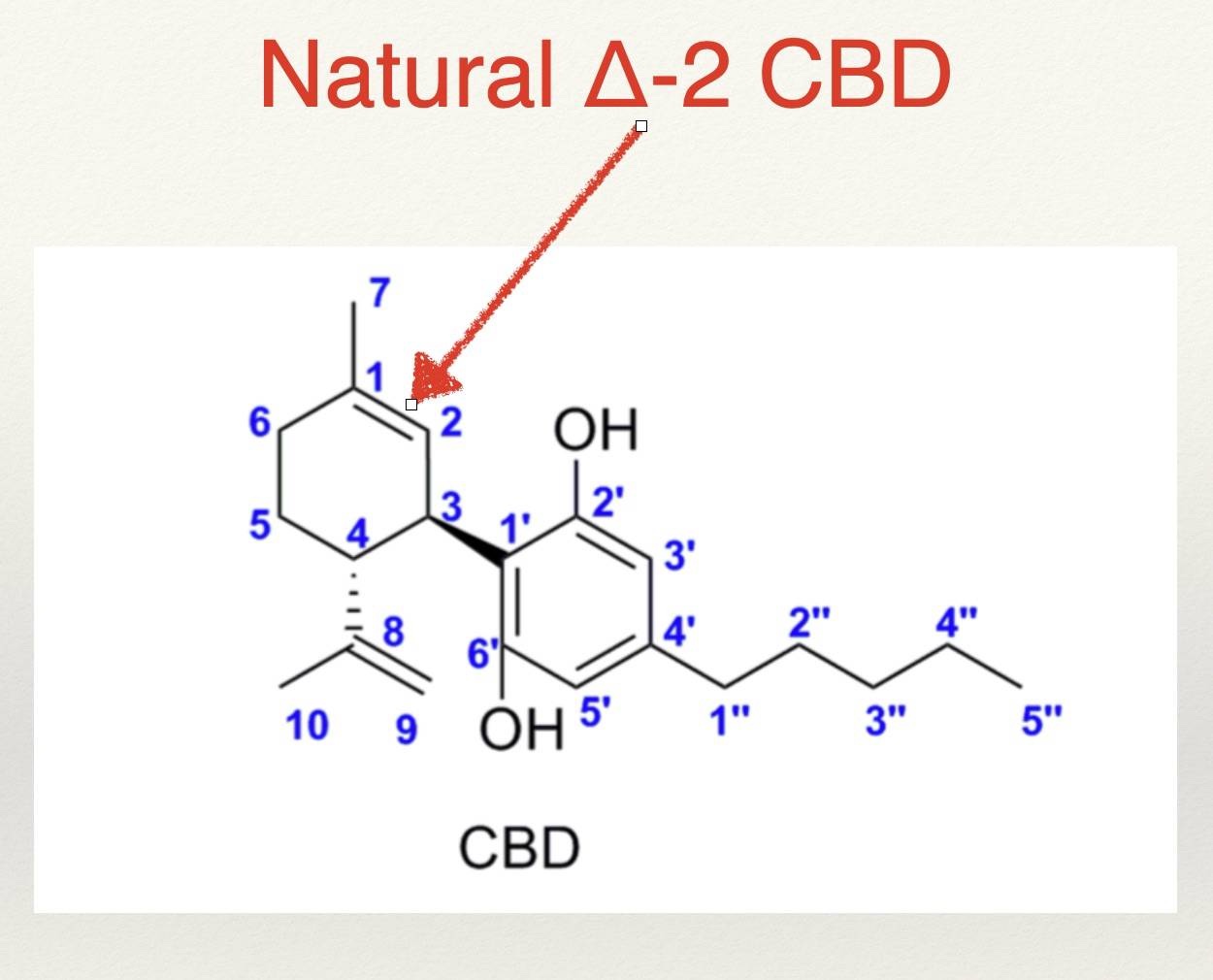
Natural vs. Synthetic CBD "Isomers"
In chemistry, isomers are molecules with the exact same number and types of atoms, but the electrons shift differently in space. The CBD that you get from the natural plant, is always an isomer is in the delta 2 (Δ-2) bonded position. However, when CBD is over processed & denatured or improperly synthesized, different isomeric “types” of CBD can be created: Δ-1, Δ-6, Δ-5, Δ-4, Δ-3. Yes, these are technically “CBD” and they will be detected as CBD on most spectrographic tests because they have the right molecular weight and shape, but they have inferior effects in the human body. It’s kind of like “trans fats.” Our DNA and our immune system “picks up” that something isn’t quite right with the molecule and responds accordingly.
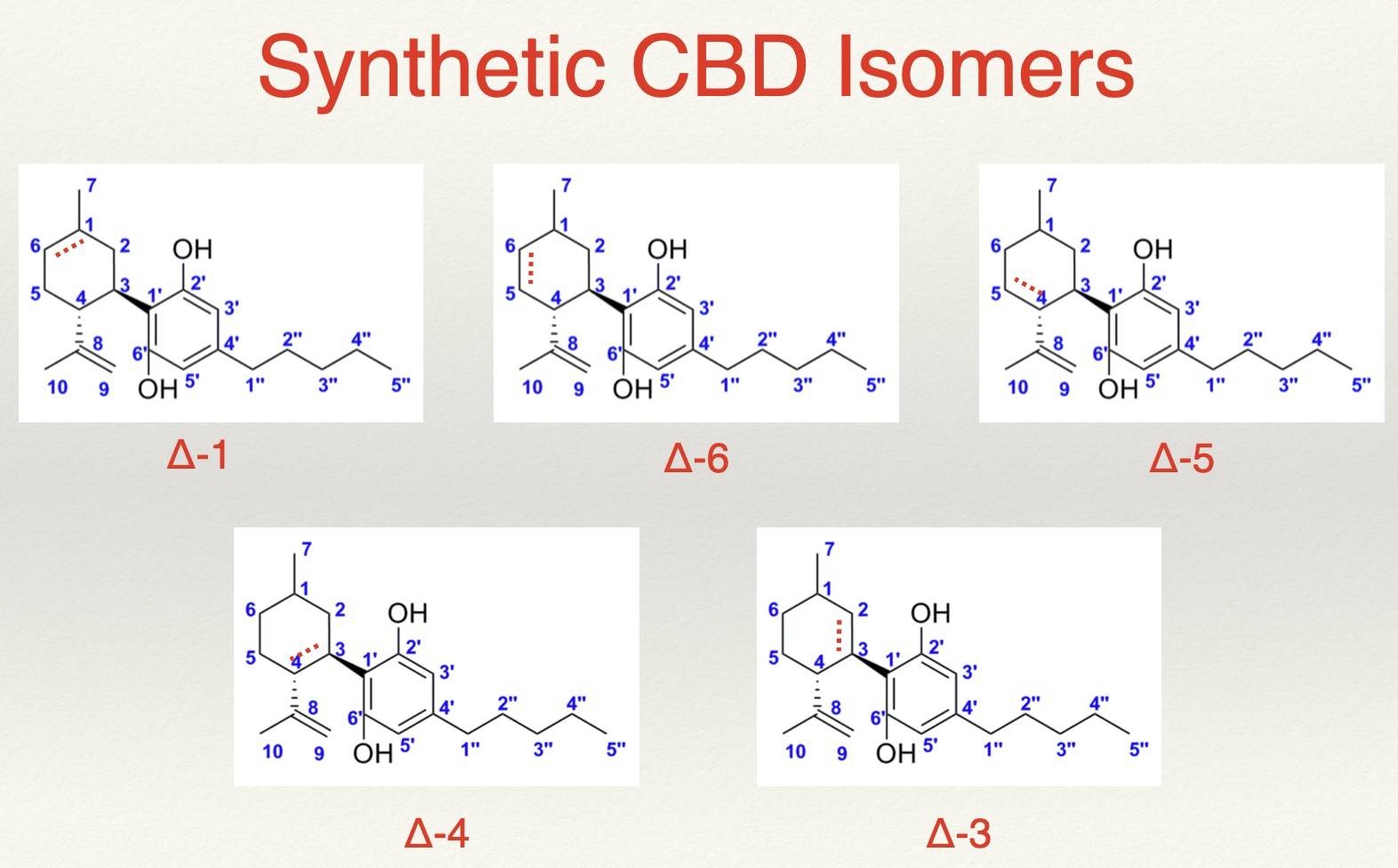
Peak Health has applied for a patent on an anti-CBD antibody called Natyam and we show which parts of the new antibody touches specific places on the Δ-2 CBD molecule, causing it to “latch on” to it. These different isomers of CBD, with the shifted double bond positions, significantly affects how the antibody molecule latches on to it. If I have a 50-50 mixture of Δ-2 CBD and Δ-6 CBD, a spectrographic lab analysis will show that this sample of CBD is “%99.96 pure CBD” because they both show up as the same peak. What this test doesn’t show is that the bond angles are different and the biological responses to it are not exactly the same!
The antibody that Peak Health created bonds with less intensity against denatured and synthetic CBDs, because the geometry of the bond angles are different.
Synthetic CBD Analogues
Growing hemp or hops as a source of cannabinoids is an expensive, land and labor-intensive undertaking. It takes a lot of space and time to create a substantial supply of natural cannabinoids. Making a synthetic CBD product is often easier and more cost efficient than to extract CBD from a plant.
There are many different isomers and analogues of CBD that in the scientific literature and they sometimes are detected in consumer products on the market. These include:
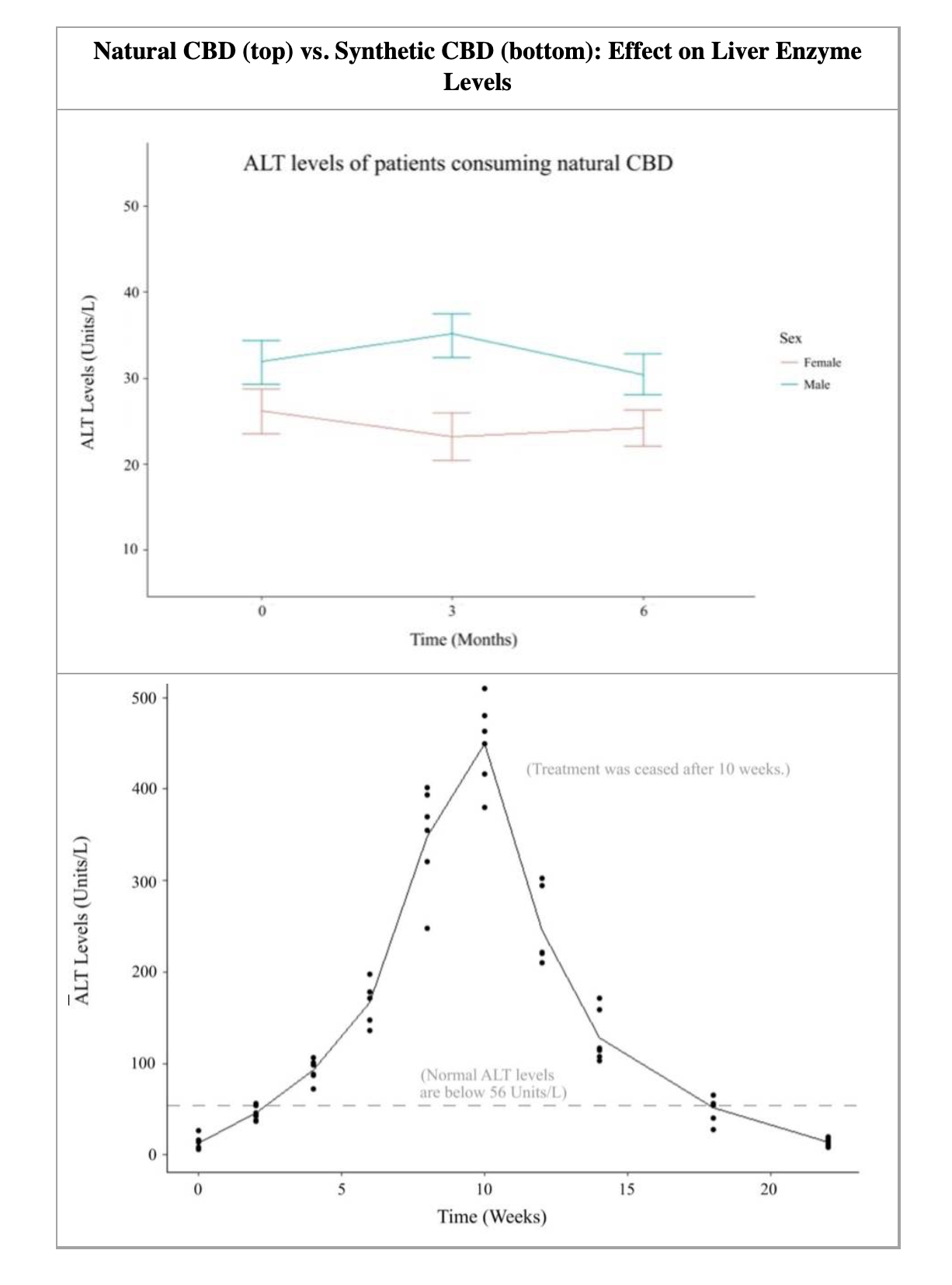
Natural vs. Synthetic CBD in Humans
We published a study in 2018 showing that synthetic cannabinoids severely elevate amino transferase levels, while natural CBD does not. Some students in India had acquired a supply of CBD that turned out to be hydrogenated CBD. We analyzed it and told them not to take it. The reason is that hydrogenated CBD stresses out the liver, causing the ALT & AST liver enzymes to rise to 10x their baseline levels over a course of 10 weeks. The good news is that when people stop taking it their liver slowly recovers back to the baseline levels.
Synthetic THC analogues are known to be dangerous. When four patients were found “freaking out” and having a bad reaction to a synthetic cannabinoid (believed to be JWH-018), tests showed their liver enzyme levels to be highly elevated (more than 1000 units/L). Those who took hydrogenated CBD for 10 weeks averaged around 480 units/L and those who took botanical CBD and no other drugs averaged liver enzymes of only 40 units/L. The only “upside” of synthetic THC is that it has powerful, noticeable effects and users can get instant feedback.
CBD, including synthetic CBD analogues, does not give you that kind of dramatic feedback so it is harder to tell immediately if it is having an effect or not. The only FDA-approved CBD for sale, by prescription, is called Epidiolex. While it comes from a natural plant, it is highly refined and it has a liver enzyme profile extremely similar to the hydrogenated CBD. Most of the people in the clinical trial for Epidiolex had a mild-to-moderate negative reaction with liver stress, which you don’t see as often with less-refined commercial CBD products.

The Danger of CBD Vapes
CBD vapes have had a number of reported negative effects. Some of these problems are caused by dangerous chemicals added to CBD vaping liquid. Other problems may be caused by pyrolysis, or burning the CBD at high temperatures, causing it to become denatured.
Future Cannabinoid Drugs: Natural vs. Synthetic
The big battle for the future of the pharmaceutical cannabinoids will be natural vs. synthetic cannabinoid drugs. The FDA-approved CBD is a natural extract but other pharmaceuticals want to go the synthetic route for stronger potency and more profits. There is an assumption that more potent is better and more likely to have therapeutic effects. In most cases it will be more likely to cause a negative reaction.
Stronger potency is not always better. Natural wild cannabis has 1 to 2% THC and lacks many of the negative side effects of high-potency hybrid cannabis (up to 30% THC). If you let high potency hybrids back into the wild and didn’t propagate individual specimens with cloning and selective breeding, the plants would lose their potency over subsequent generations and the THC levels would come back down.
Testing CBD: GC/MS vs. X-Ray Crystallography
The most popular lab analysis equipment (GC/MS) can detect mass but not quality. It cannot tell which CBD isomers are bioactive or “high quality.” X-ray crystallography is a more advanced & expensive testing method, that is rarely used by commercial labs at the time of this writing. This method of testing is extremely precise, it can detect isomers and bond angles and natural compounds vs. synthetics. However, it cannot detect bioactivity.
Measuring the Bioactivity of CBD
When CBD is injected into a mice or rabbits, there are a whole bunch of antibodies that get produced in reaction to that antigen. We isolated these heterogeneous antibodies and found one that has the strongest affinity to the CBD. We called it Natyam, which means dancing in Sanskrit, and we have filed for a patent on it.
CBD that is of the highest quality and measured to be 100% bioactive, would have a certain amount of Natyam bound to it. This is a good method for measuring the bioactivity of CBD. So if the CBD you are measuring is expected to have a reading of 88 and you only get a reading of 20, your measured bioactivity is 22.7% (100/88*20.) Getting polyclonal antibody is easy. Isolating the perfect monoclonal antibody is a lot more work, tedious and difficult. To convert this monoclonal antibody into a “hybridoma”, maintain it so that it stays live and healthy, and harvest them for large volume monoclonal antibody production is an enterprise in itself. Peak Health not only has a patent pending for the MCA, Natyam, but also has an industrial hybridoma processing factory that manufactures it.
Ensuring CBD Quality
All CBD is not created equal. We’ve analyzed CBD from hemp & hops flowers, we’ve looked at it from the stems and leaves. We found the flowers to have, by far, the highest bioactivity. When we calculated the estimated bioactivity of stimulated (synthetic or denatured) CBD, it scored extremely low, even lower than hemp bark. Botanists are not at all surprised by this. The life of a plant, and the propagation of its species, is in the inflorescence. The bark and stem only provide protection and structure to move nutrients.
There is more and more synthetic CBD starting to show up on the markets, both listed and unlisted. The main tenets to keep in mind are:
- Natural CBD provides a far more desired response in the human body than synthetic CBD.
- Flowers have higher bioactive molecules, like CBD, than leaves or stems. What smells more fragrant, a flower or the stalk?
- Vertically integrated vendors have more quality control over their products
- GC/MS and common lab tests measure quantity but not quality of CBD.
- X-ray crystallography detects natural vs. synthetic CBD
- Synthetic CBD scores very poorly on antibody bioactivity tests
- Natural CBD does not significantly elevate liver enzyme levels.
- Simulated (synthetic or denatured) CBD gradually elevates liver enzymes levels but it can be reversed if discontinued.
What the people are looking for is natural CBD from high-quality sources. The hemp industry is highly fragmented. Farmers grow the hemp. Aggregators buy the crops, aggregate them and sell them to oil/extract processors. Multiple vendors buy these oils. Some of these oils are bought by by isolate manufacturers (via middle men) who convert the oils to CBD isolate. Quality is obtained by following a disciplined methodology all the way in the growth and production process. This is not possible when multiple fractions, with competing interests are in the production chain. This is one major reason scientific innovation and quality standards are difficult to implement in the hemp industry. Too many cooks in the kitchen!
Hops CBD Industry Avoids Quality Control Issues
So far, the hops CBD production is a vertically integrated operation within the same organization. Constant innovation, scientific testing and learning has allowed for the applications of multiple patents and a uniquely qualified product. Peak Health is to the CBD market what Apple is to the technology market.
